As you add light, shadow is removed (carving out shadows); in addition, it is a 24 hour cycle, where the light and dark are constantly replacing each other.
2. Daily and Seasonal Cycles (plants change due to changes in their environment): leaves, the sunflower growing towards the sun
3. Multiple uses for one element: Thorns as modified branches, photosynthetic stems (the first plants on earth - evolving from seaweed); the yellow pitcher plant (photosynthetic leaves and bug catcher)
4. Parasitic vines - creeping towards detected shadows (this is where the tree canopy is) - could be thought of a way to carve out shadow.
5. Venation - 40 types found in nature - how do you begin to test which is most efficient - can this relate to movement in an educational institute?
6. The Virus: deforming shapes under specific algorithms - could be thought of a way to being to carve out or morph shadow on the site
7. Lithops: program of building pushed to exterior circumference and capturing light through the openings according to specific day and time of the year (i.e. a playground should be lit fall to spring from noon to one)
8. Slightly varying components that make up the larger whole - similar to the oak tree, which has two general types of leaves: shade and light.
9. Building as a plant in the sense that it is stationary - how can a building "change" during the day and seasons like plants - how light is used is definitely a solution.
10. All elements in plants have a purpose that is part of the form of the larger whole (form and function) - the accordian shape of cacti - expanding after a storm to cary more water.
A time lapse video showing how multiple organisms interact with each other and changes in the environment:
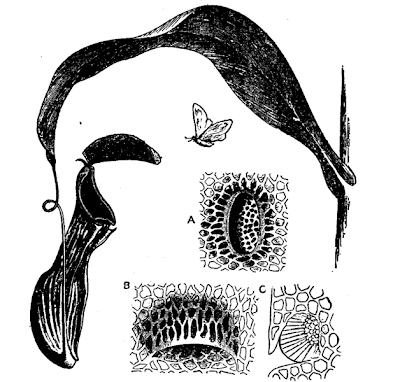
Diagram of a pitcher plant from the Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition. Pitcher of Nepenthes distillatoria. A: Honey-gland from attractive surface of lid. B: Digestive gland from interior of pitcher, in pocket-like depression of epidermis, opening downwards. C: Traverse section same.
Great summary from our trip to the Botanical Garden.
ReplyDelete